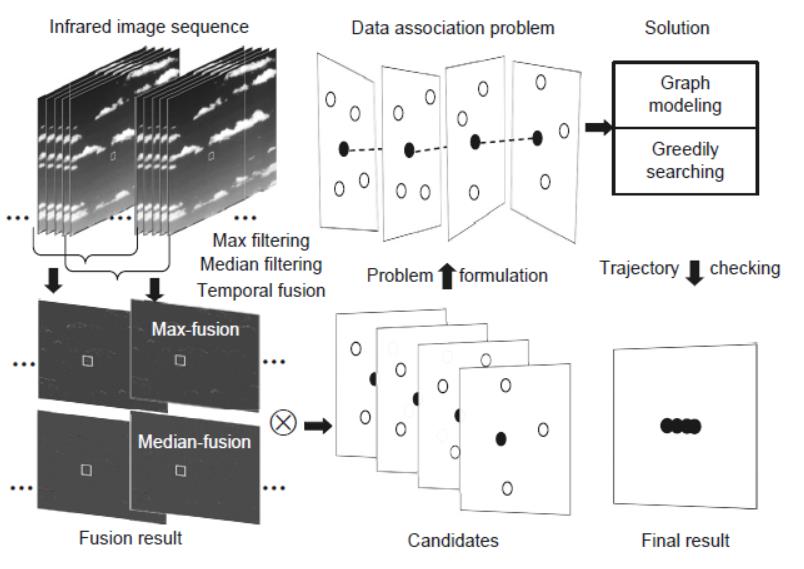
The special characteristics of slowly moving infrared targets, such as containing only a few pixels, shapeless edge, low signal-to-clutter ratio, and low speed, make their detection rather difficult, especially when immersed in complex backgrounds.
To cope with this problem, we propose an effective infrared target detection algorithm based on temporal target detection and association strategy. First, a temporal target detection model is developed to segment the interested targets. This model contains mainly three stages, i.e., temporal filtering, temporal target fusion, and cross-product filtering. Then a graph matching model is presented to associate the targets obtained at different times. The association relies on the motion characteristics and appearance of targets, and the association operation is performed many times to form continuous trajectories which can be used to help disambiguate targets from false alarms caused by random noise or clutter. Experimental results show that the proposed method can detect slowly moving infrared targets in complex backgrounds accurately and robustly, and has superior detection performance in comparison with several recent methods.
Bright cloud clutter and strong noise can be suppressed based on the proposed temporal target detection model, and the temporal filtering methods are superior to the spatial filtering methods when detecting small targets immersed in bright cloud backgrounds.
@article{gao-etal-2016-detecting,
author = {Gao, Jingli and Wen, Chenglin and Bao, Zhejing and Liu, Meiqin Liu},
title = {Detecting slowly moving infrared targets using temporal filtering
and association strategy},
journal = {Frontiers Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng.},
volume = {17},
number = {11},
pages = {1176--1185},
year = {2016},
doi = {10.1631/FITEE.1601203},
}
This work is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China.